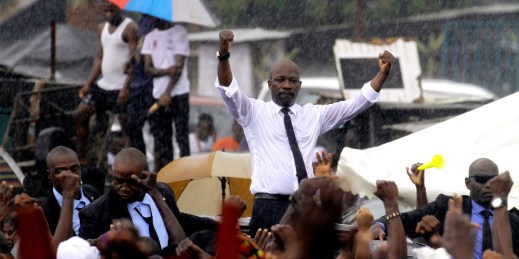A controversial referendum in Central African Republic could allow President Faustin-Archange Touadera to run for a third term. International media has focused on the role Russia, Rwanda and CAR’s other international partners play in the political standoff. But ultimately local actors will determine if Touadera succeeds or fails.